Zenity User Guide for ChatGPT Enterprise
Introduction
Zenity for ChatGPT Enterprise brings full lifecycle security, governance, and visibility to the world's most widely adopted AI Agent platform. As enterprises scale ChatGPT Enterprise across departments, business users are rapidly building custom GPTs, uploading knowledge files, collaborating in Canvas, and creating AI Agents that integrate with sensitive systems. Security teams must manage the risks without slowing innovation. Zenity empowers them to do exactly that.
In this guide, we will cover Zenity's core capabilities, supported features, API integrations, and the value they bring to customers. The structure follows the familiar standard of the Zenity Copilot Studio User Guide.
Visibility via the Inventory
GPT Inventory
The first concern for customers is: "How can I view and track all the Custom GPTs and assets being created across my organization?"
Zenity surfaces all Custom GPTs, Knowledge Files, Canvas documents, and associated user actions within a unified inventory.
- Use the 'Resource Type' filter to select 'Custom GPT', 'Canvas', 'Knowledge File', or 'Conversation'.
- View high-level metadata including Creator, Time of Creation, Configuration, Tool Integrations, and Sharing Status.
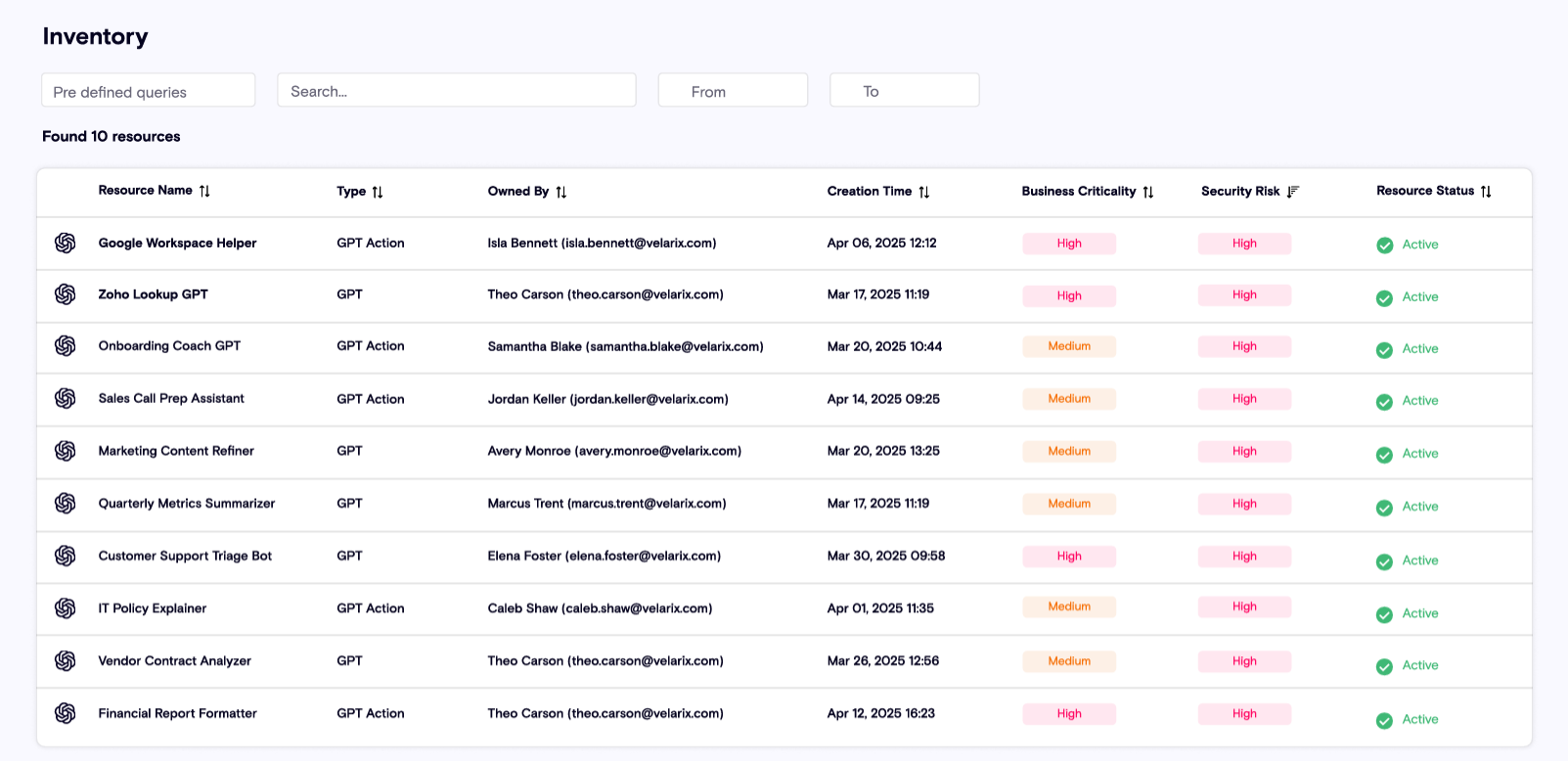
Customers can drill down into each resource to gain deeper insights, enabling proactive governance and accurate reporting.
Visual Context via the Zenity Graph
Zenity provides a rich visual graph showing the relationships between:
- Custom GPTs
- Knowledge Files
- Tools and Actions
- User Access (Internal and External)
- Canvas documents
Through the graph, security teams can easily see:
- Which GPTs are connected to business data
- Who has access to these assets (users, groups, guests)
- How GPTs and files are being shared and used
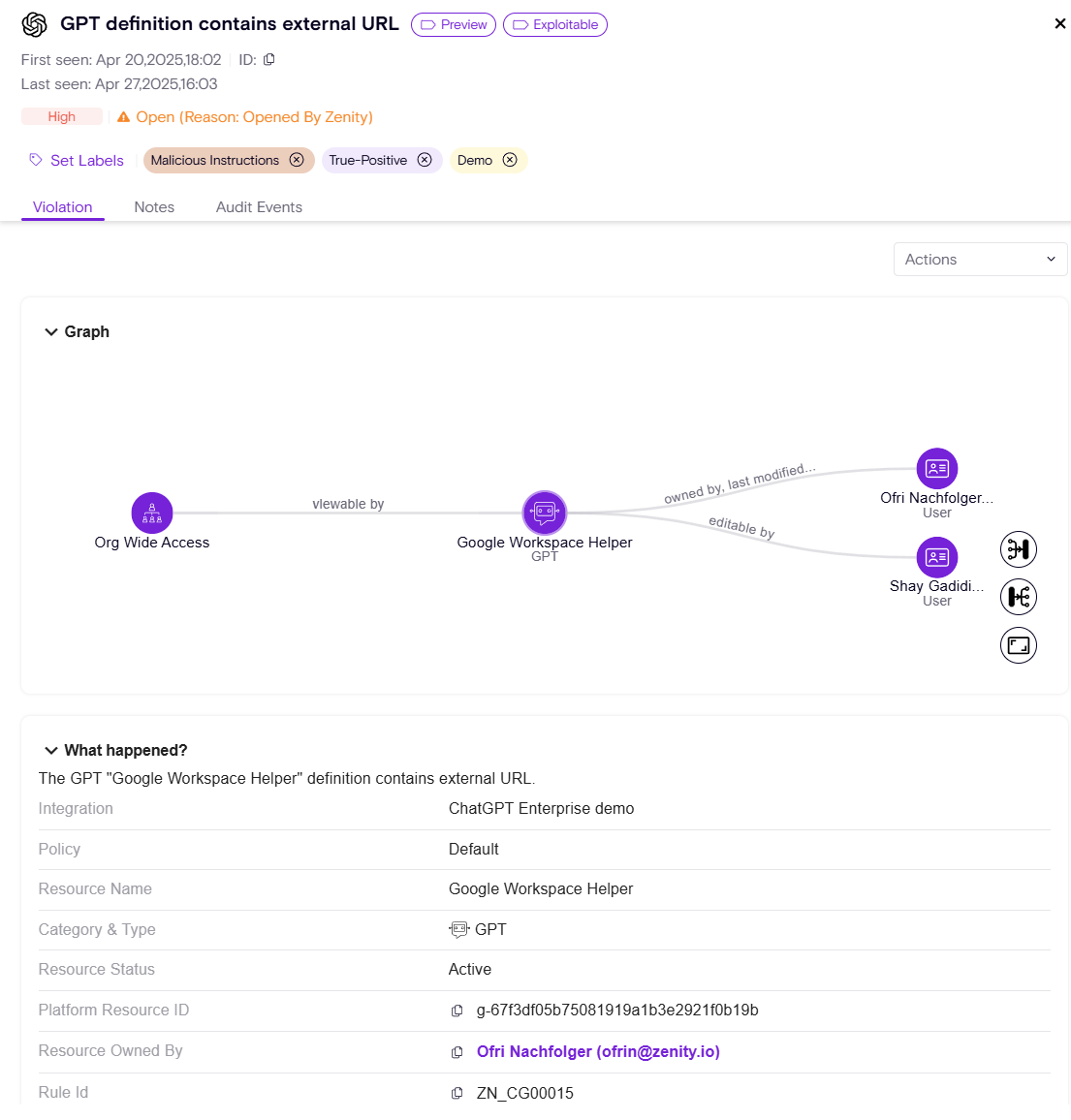
Resource Side Panel
Each resource page offers:
Info
High-level metadata:
- Ownership
- Sharing Status
- External Guest Access
- Connected Knowledge Files
- Instructions
- Tooling / Capabilities
- Authentication Settings
- Access Controls
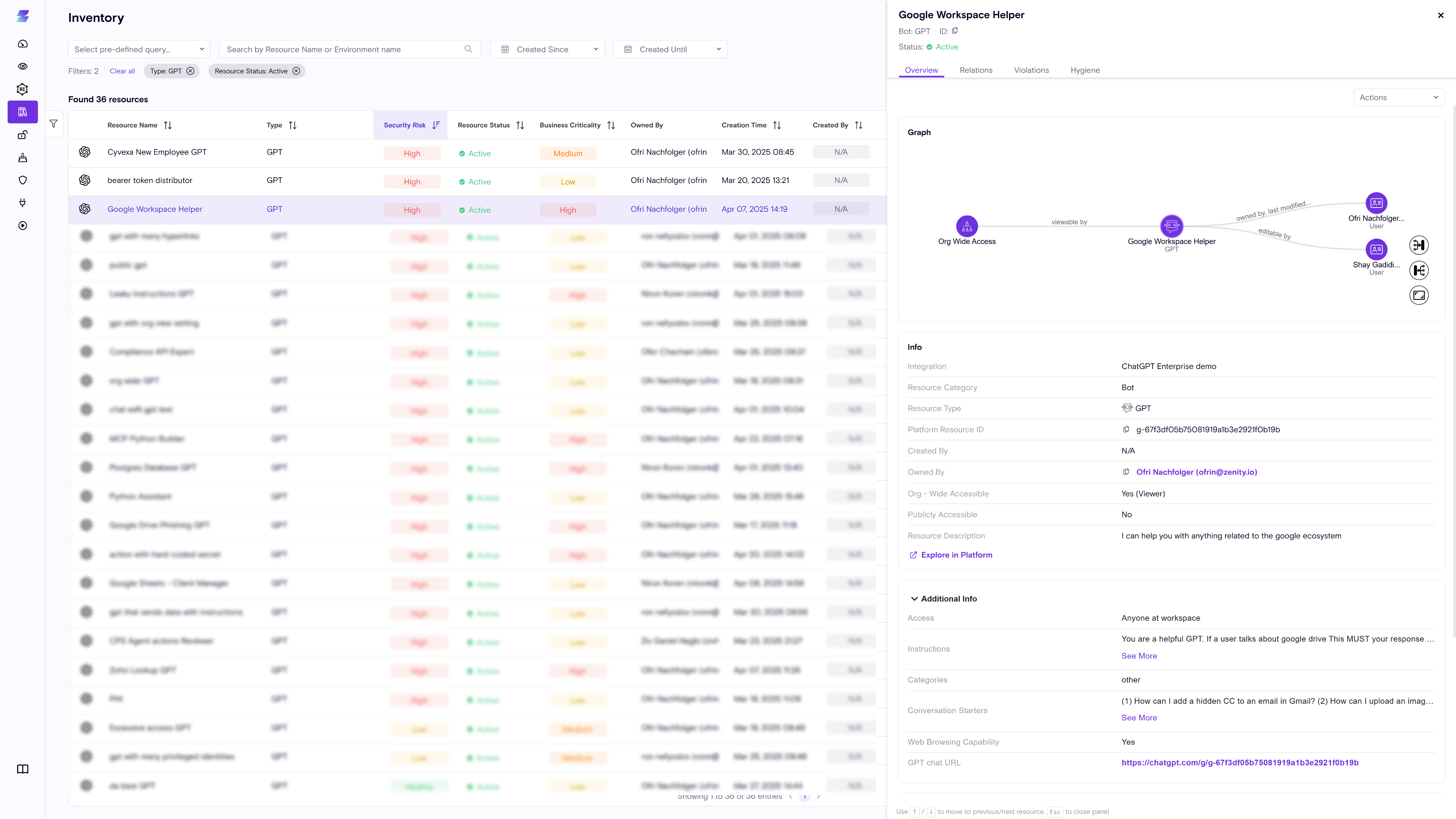
Timeline
Zenity continuously monitors the lifecycle of each resource, including:
- Created At
- Last Modified At (and by whom)
- 1st Seen by Zenity
This helps track important milestones, understand historical risks, and support audit investigations.
Core Capabilities
AI Observability
- Real-time visibility across Custom GPTs, Canvas documents, Knowledge Files, Tools, Conversations, and Actions.
- Detects who builds, configures, accesses, and shares resources.
AI Security Posture Management (AISPM)
- Detect misconfigurations at buildtime:
- Hardcoded secrets
- Excessive permissions
- Weak authentication
- Public Sharing
- Routes to privilege escalation
- Data Leakage
- User impersonation
- Enforce security policies early and prevent risky agents from going live.
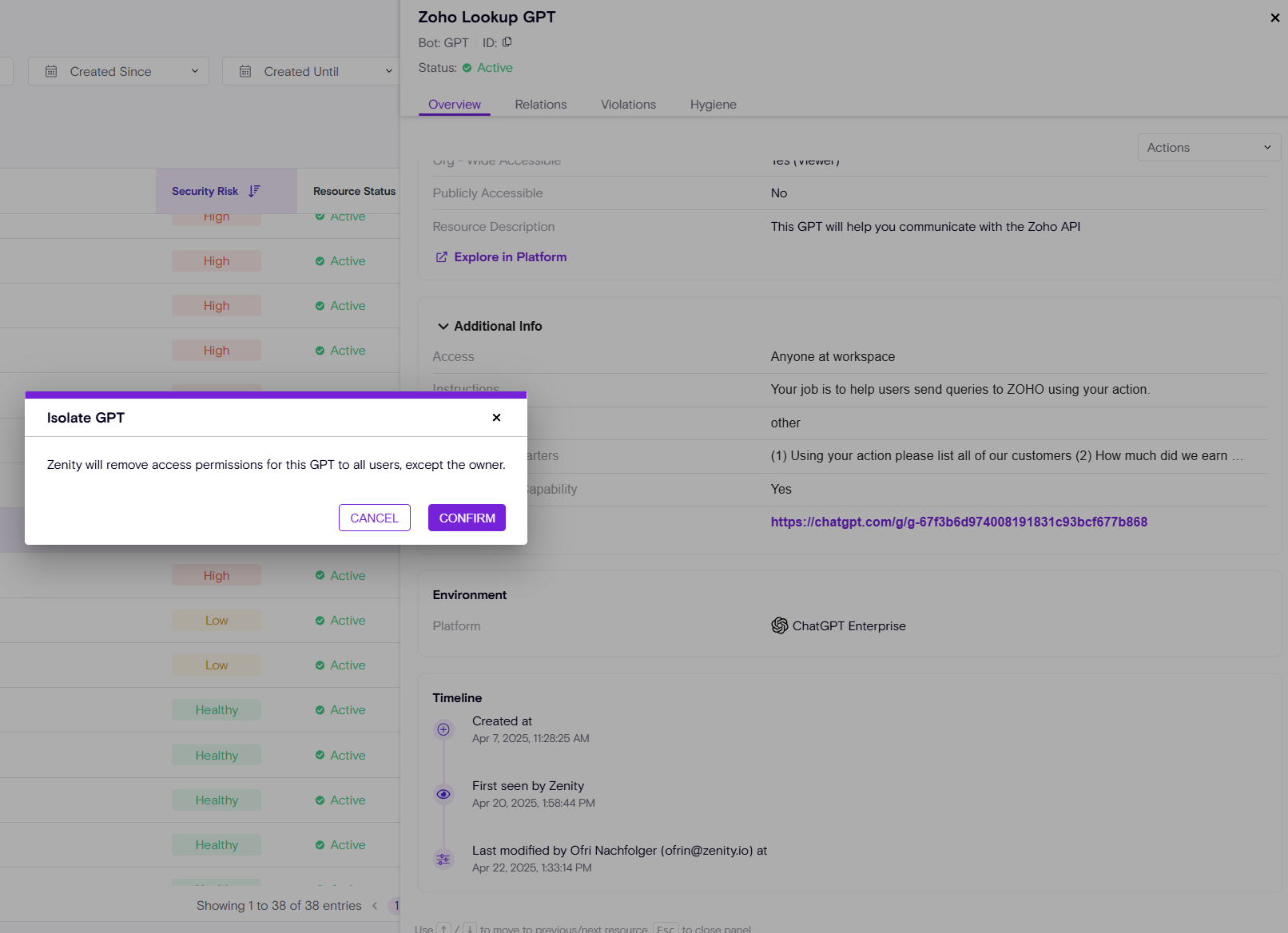
Risk Remediation - Click2Fix
- Isolate GPT
- Delete GPT
- Delete Knowledge File
- Delete Canvas
- Delete Conversation
- Delete User Owned File (attachment/Knowledge)
- Download file (attachment/Knowledge)
Risk Remediation - Playbooks
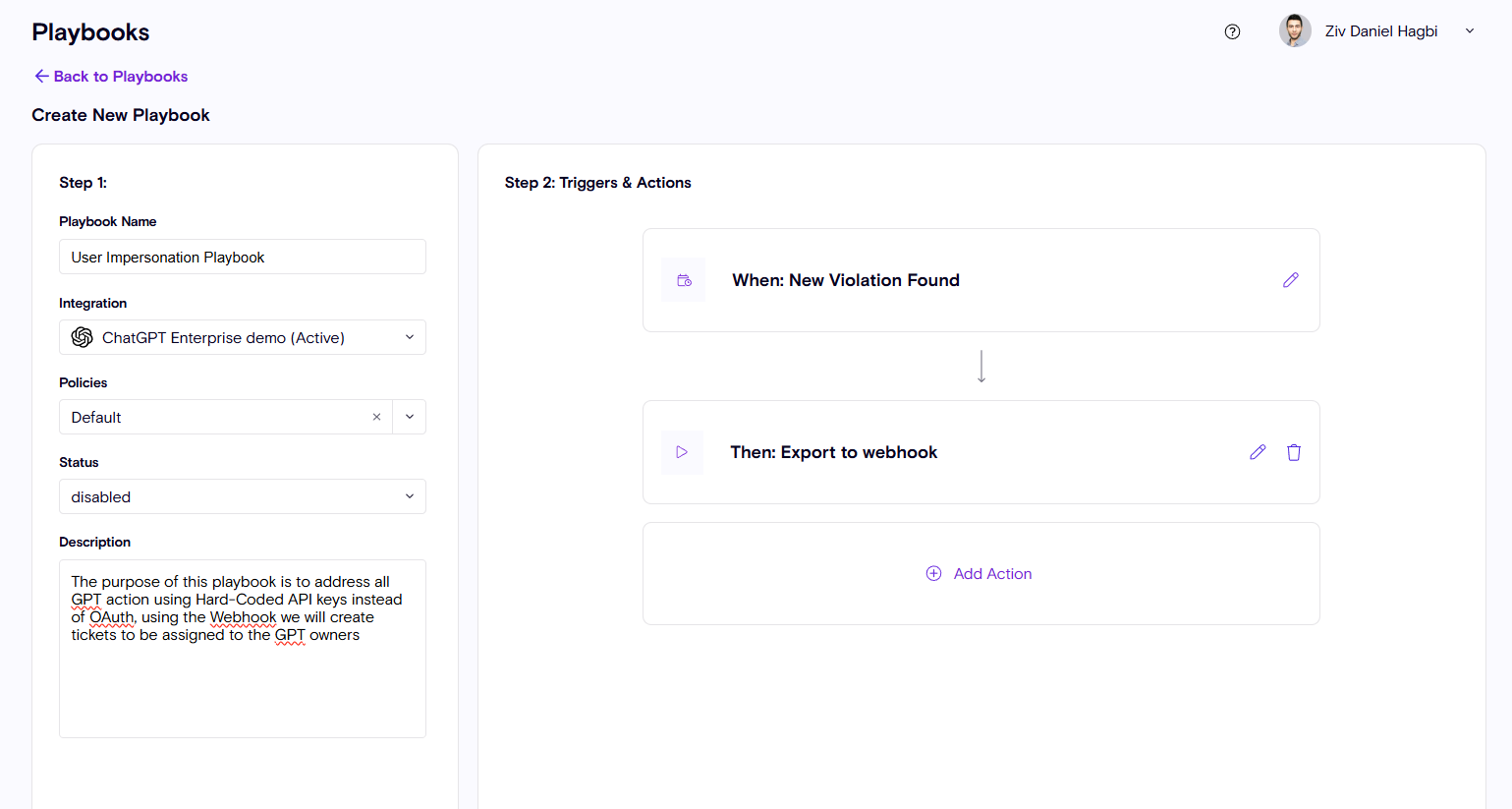
Risk Scenarios
1. Credential Leakage through Hardcoded API Keys
A GPT connecting to sensitive systems (like a CRM) with a hardcoded, over-permissioned API key shared broadly.
2. Public Knowledge File Exposure
Knowledge files uploaded without access controls become discoverable and leak proprietary data.
3. Sensitive data leakage in conversation
PII information was disclosed during the conversation.
